tear duct obstruction test|blocked duct diagnosis : exporter exporters exporting Dye disappearance test: This test uses dyed eye drops to determine if your tear ducts are blocked. If the eye drops disappear within 5 minutes, there’s no tear duct obstruction.
ak888bet วงการเดิมพันออนไลน์เรียกได้ว่ากำลังบูมและมาแรงที่สุดในปัจจุบัน ช่องทางการสร้างรายได้รูปแบบใหม่ที่คนให้ความสนใจ แจกวันละ 100 บ.
{plog:ftitle_list}
House, M.D. ou simplesmente House (também conhecida no Brasil como Dr. House) é uma série médica norte-americana criada por David Shore e exibida originalmente nos Estados Unidos pela Fox de 16 de novembro de 2004 a 21 de maio de 2012. Seu personagem principal é o Dr. Gregory House, interpretado pelo ator inglês Hugh Laurie. A série passa-se no fictício hospital universitário .
The symptoms of a blocked tear duct can include: 1. Watery eyes (epiphora). 2. Gooey or crusty buildup on your eyelids or in your eyelashes. 3. Frequent rubbing of your eye or face around the blocked duct. 4. Redness and swelling (from rubbing). 5. Blurred vision. These blockages can also make it easier to . See moreTear duct blockages can happen for a few different reasons. Some are congenital, meaning you have them when you’re born. Others develop later in life. See moreA blocked tear duct is just the kind of place where bacteria find it easy to grow, so bacterial infections or abscesses are the main possible complications of a . See more Tests used to diagnose a blocked tear duct include: Tear drainage test. This test measures how quickly your tears are draining. One drop of a special dye is placed on the .
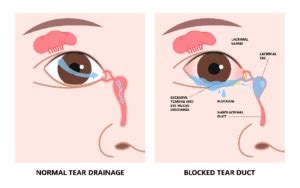
Secondary acquired nasolacrimal duct obstruction (SANDO) is an obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct caused by a secondary etiology, as opposed to the idiopathic primary . Dye disappearance test: This test uses dyed eye drops to determine if your tear ducts are blocked. If the eye drops disappear within 5 minutes, there’s no tear duct obstruction. When you have a blocked tear duct, your tears can't drain normally, leaving you with a watery, irritated eye. The condition is caused by a partial or complete obstruction in the .Nasolacrimal duct obstruction is a blockage or stenosis of the tube that collects tears from the inner corner of the eye and drains them into the nose. It causes epiphora, irritation and blurred .
When tear ducts become blocked, tears build up. These irritate the eyes, increasing the risk of infection and causing painful swelling. Read more about blocked tear ducts here. Your ophthalmologist diagnoses a blocked tear duct using a number of tests, including a complete medical eye exam. He or she will discuss your medical history and . Nasolacrimal duct obstruction (NLDO) or dacryostenosis is the most common disorder of the lacrimal system, and approximately 6 to 20 percent of newborns exhibit .Blocked tear ducts are caused by a partial or complete obstruction in the tear drainage system. This condition is almost always is correctable. Treatment depends on the cause of the .
blocked tear duct test
Secondary Acquired nasolacrimal duct obstruction is nasolacrimal duct obstruction caused by a defined non-congenital etiology. . Dye disappearance test: examiner administers fluorescein drops and observes under cobalt blue filter. . Thale, A. B., Hallmann, U. J., Schaudig, U. & Tillmann, B. N. The cavernous body of the human efferent tear .
It's usually because the tear duct hasn't had enough time to develop properly yet, and tends to resolve itself. . Takahashi Y, Kakizaki H, Chan WO, et al; Management of congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction. Acta Ophthalmol. 2009 Jul 21. Resolution of congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction with nonsurgical management; Arch Ophthalmol . Dacryocystitis refers to an infection of the tear sacs, which are part of the tear drainage system in the eye. Tears drain from each eye through small canals (drainage canals), a tear sac, and a tear duct.Drainage canals are .
Pain at the tear duct or surrounding area; Causes of a Blocked Tear Duct In most cases, the cause of a blocked tear duct is not known. Other times, the blockage can be caused by health problems such as: Anatomical problems you were born with; Chronic nasal and sinus inflammation; Obstruction from a tumor; Trauma to the nose; Conjunctivitis When a blocked tear duct doesn't open on its own, these techniques can help infants and adults: Massage. One of the easiest ways to fix a blockage in babies (or adults) is to massage the lacrimal . Nasolacrimal duct obstruction is usually caused by persistence of a membrane at the distal valve of Hasner. The primary symptoms are epiphora and periocular crusting and discharge due to infection of . The presence of enlarged tear lakes and periocular discharge helps confirm the diagnosis. The vast majority of infants with these findings . The incidence of nasolacrimal duct obstruction is 20.24 per 100,000.[2] . (10 micrograms of TC-99) in the inferior fornix and tear flow with a scintigram gives physiological information of tear flow. The test involves imaging the lacrimal system sequentially to capture the physiological flow of the tracers through the lacrimal system. This is .
blocked tear duct system
Approximate Synonyms. Acquired dacryostenosis; Dacryostenosis; Obstruction of nasolacrimal duct; ICD-10-CM H04.559 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v 42.0):. 124 Other disorders of the eye with mcc or thrombolytic agent; 125 Other disorders of the eye without mcc; Convert H04.559 to ICD-9-CM. Code History. 2016 (effective 10/1/2015): New code (first .
This new route bypasses the duct that empties into your nose (nasolacrimal duct), which is typically the blockage site. Stents or intubation typically are placed in the new route while it heals, and then removed three or four months after surgery. The steps in this procedure will vary depending on your particular tear duct blockage. 24. Wearne MJ, Pitts J, Frank J, Rose GE. Comparison of dacryocystography and lacrimal scintigraphy in the diagnosis of functional nasolacrimal duct obstruction. Br J Ophthalmol 1999;83:9:1032-1035. 25. Yeatts P. Acquired nasolacrimal duct obstruction. Ophthalmol Clin North Am 2000;13:4:719.
water permeability test for concrete din 1048
Tear duct massage can help open the blocked duct so tears can flow through it. How to Massage the Tear Duct. Wash your hands with soap and warm water before and after the massage. Place the tip of your index finger against the side of your child’s nose, in the corner of the eye with the blocked tear duct (Picture 2).Then, they drain though the tear ducts. When a tear duct is blocked (a blockage), the tears can't drain. Many babies are born with a tear-duct blockage. Blocked tear ducts in babies usually clear up with little or no treatment by the time a child is 1 year old. What Are the Signs & Symptoms of a Tear-Duct Blockage? A child with a blocked tear .
Nasolacrimal duct obstruction is the obstruction of the nasolacrimal ducts . A silastic tube or stent may be employed along with probing to maintain tear duct patency. [6] . particularly asymmetric clearance of the dye from the tear meniscus over a 5-minute period indicate an obstruction. If the dye disappearance test result is normal . Your ophthalmologist will also use certain tests to examine the tear drainage system for blockage. A special fluid is flushed into the affected tear duct opening and, if the fluid cannot be tasted in the throat, a blocked tear duct is diagnosed. Other tests may include an X-ray or CT scan of the tear duct area (called a dacryocystogram). About 6% of babies born have congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction (NLDO). Dacryocystitis happens in about 1 in 3,884 live births. It’s more common in females than in males because their passageways are narrower. . A blockage in your tear duct causes dacryocystitis. These blockages disrupt the flow of tears from your eyes into your nasal .
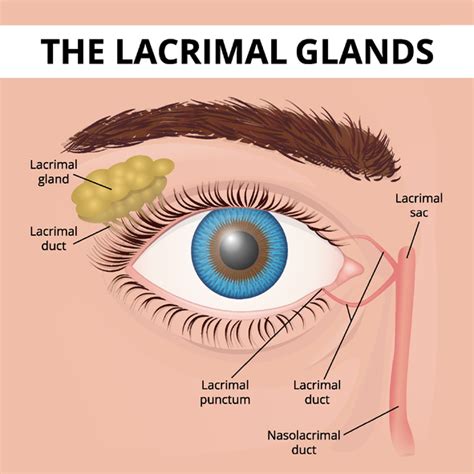
The nasolacrimal system consists of a series of narrow tubes that allow tears to drain from the eye. This system allows excess tears to drain from the eye to the nose and mouth. In some cats, this nasolacrimal duct can become obstructed. Most affected cats have excessive watering of the eyes, or reddish-colored tear staining of the face.A blocked tear duct can occur in one or both eyes. The blockage may be present at all times, or it may come and go. . This condition is called dacryostenosis or congenital (present at birth) lacrimal duct obstruction. Tears help clean and lubricate the eye and are produced in the lacrimal gland located under the bone of the eyebrow. Tears .What is a tear duct obstruction? Tears are made in the lacrimal gland on the upper outer corner outside the eye. Tears normally drain from the eye down to the nose through the tear duct or nasolacrimal duct. If one looks in the mirror the openings of the tear duct system can be seen in the corners of the upper and lower eyelids closest to the nose.
blocked tear duct surgery
A leading cause of blocked tear ducts in adults is infection of the eyes, tear duct system, or nasal passages. An injury or trauma to the eye can also lead to a blocked tear duct. Nasolacrimal duct obstruction: Blockage of the tear drainage duct, whether due to congenital reasons, infection, inflammation, or trauma, can cause persistent watery eyes. . Additional diagnostic tests, such as Schirmer's test for tear production, slit-lamp examination, fluorescein staining, and imaging studies, may be necessary to establish .
When you have a blocked tear duct, or a nasolacrimal duct obstruction, your tears can't drain normally, leaving you with a watery, irritated eye. . Tests to diagnose a blocked tear duct include: Tear drainage test. Called a dye disappearance test, this test measures how quickly your tears are draining. One drop of a special dye is placed in . See your doctor if your symptoms worsen. Physical examination by a medical professional is required in order to diagnose a blocked tear duct. While simple inflammation might be causing the blockage, it could also be a tumor or another serious medical problem, so it's important to see your doctor. To test for a blocked tear duct, the doctor will flush out the eye . Chronic nose infections: Repeated nasal infections, such as chronic sinusitis, can obstruct the tear ducts.; Abnormal development of the skull and face: People with certain skull or facial anatomical differences, like Down syndrome, are more likely to be affected by a blocked tear duct.; Age-related changes: Changes like narrowing of the punctal openings, tiny . Tear duct probing. If a tear duct doesn't open on its own by your baby's first birthday, the doctor can place a thin probe into the puncta to open the tissue covering the duct. Balloon catheter .
blocked tear duct repair
blocked tear duct obstruction
Another test for PANDO is to trace the movement of dye through the lacrimal drainage system in one of two ways: 1) dacryocystography, where dye is injected in the tear duct and traced with X-ray and/or CT scan, or 2) dacryoscintigraphy, where a radiotracer eye drop is placed in the conjunctival cul-de-sac and its movement is recorded over time . A cotton swab can be inserted into the nose to see if any dye has passed through the tear duct. This test can help your doctor tell whether your tear duct is blocked completely or partially. . there may still be excessive tearing or cloudy drainage from block tear ducts. In infants, the obstruction that causes an infection is commonly .
Causes of Nasolacrimal Duct Obstruction. Failure of the thin tissue at the end of the tear duct to open normally is the most common cause. In adults, a blocked tear duct may be due to an injury, infection or a tumor. (Blocked tear ducts are very common in newborns, but they usually get better without any treatment during the first year of life.)
blocked tear duct eye test
WEBSe quiser saber sobre Fortune Ox onde jogar, a versão demo do Fortune Ox está disponível em vários cassinos online que oferecem jogos da PGSoft. Muitos desses .
tear duct obstruction test|blocked duct diagnosis